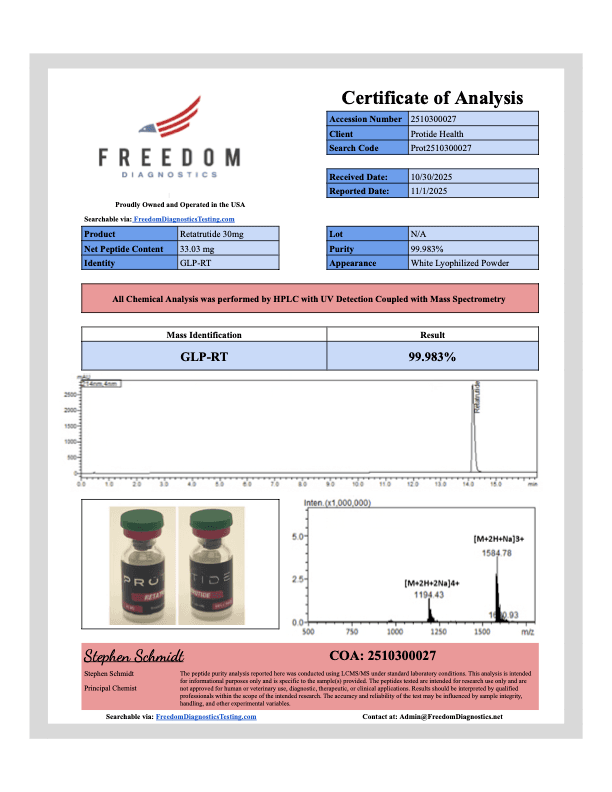
GLP-3 30mg
$260.00
GLP-3 peptide 30mg is an advanced triple hormone receptor agonist designed for high-precision metabolic research. By simultaneously targeting the GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors, this synthetic compound allows researchers to investigate complex pathways involving appetite regulation, energy expenditure, and glycemic control in laboratory models. Each vial contains 30mg of high-purity, lyophilized powder.
In stock
Free shipping on orders over $149!
- 99% Purity
- Third-Party Tested
- Secure Payments
- Free BAC Water
- Satisfaction Guaranteed
What is GLP-3?
GLP-3 peptide is a synthetic research peptide designed as a “triple agonist,” meaning it can activate three different hormone receptors involved in metabolism. In this format, GLP-3 peptide 30 mg per vial is supplied as a lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder for controlled laboratory and preclinical research, not for human use. Early clinical studies have explored GLP-3 peptide in obesity and metabolic health models, but it remains an investigational compound. PubMed
Each vial contains 30 mg of GLP-3, allowing labs to design flexible protocols across a range of in vitro and in vivo models. Because it targets GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors, researchers are especially interested in how it may influence body weight, energy use, blood sugar markers, and liver fat in experimental settings. e-ENM
Peptide type: Single peptide; synthetic triple hormone receptor agonist explored in metabolic and liver research models.
Vial content: 30 mg per vial, supplied as lyophilized powder for reconstitution in the lab.
Primary research focus: Metabolic, weight, and liver fat models (obesity, glucose regulation, and fatty-liver pathways in preclinical and clinical research). PubMed
GLP-3 Peptide Overview & Key Properties
GLP-3 peptide is a fully synthetic molecule modeled on the body’s own incretin and glucagon hormones. It is designed to activate three targets at once: the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor, the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor, and the glucagon receptor. PubMed
These receptors help regulate appetite, blood sugar, and energy use in metabolic pathways. In research, this “triple agonist” profile allows GLP-3 to be used as a tool compound for studying advanced metabolic control, weight-change trajectories, and liver fat dynamics in both animal and human trial models. PMC
In typical lab practice, GLP-3 peptide 30 mg per vial is shipped as a lyophilized powder and stored in cool, dry, dark conditions until reconstitution, in line with standard operating procedures (SOPs) for research peptides.
Peptide class or family: Triple hormone receptor agonist (GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon), part of the newer generation of incretin-based research peptides. PMC
Vial content and typical lab handling: 30 mg lyophilized powder per vial, to be reconstituted with a suitable sterile solvent according to lab SOPs.
Suggested storage concept in lab settings: Keep cool, dry, and away from light; use appropriate cold-chain storage before and after reconstitution as directed by institutional guidelines.
Common research models: Metabolic and obesity models, type 2 diabetes models, and fatty liver (MASLD/NAFLD) models in animal studies, in vitro systems, and human clinical research settings. PubMed
GLP-3 Mechanism of Action
GLP-3 is designed to work by activating three key metabolic receptors at the same time: GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors. GIP and GLP-1 are “incretin” hormones that signal after meals; they help the body release insulin in a glucose-dependent way, support feelings of fullness, and slow stomach emptying. Glucagon normally raises blood sugar and also affects fat burning and energy use. e-ENM
By combining these three signals into one peptide, GLP-3 may increase insulin release when glucose is high, reduce appetite, and boost energy expenditure in research models. In clinical trials in people with obesity and type 2 diabetes, this triple-agonist pattern has been linked to large changes in body weight, improved glycemic markers, and substantial reductions in liver fat, though these findings remain investigational and do not translate into approved medical use. PubMed
GLP-3 Peptide Research
1. GLP-3 and Metabolic Health Models
One of the best-known areas of GLP-3 peptide research is obesity and metabolic health. A phase 2, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in adults with obesity found that GLP-3 produced very large average weight reductions over 48 weeks, with higher doses approaching roughly one-quarter body-weight reduction in some groups. PubMed
Researchers observed dose-dependent changes in body weight and metabolic markers such as blood sugar and lipids. These data position GLP-3 as a powerful tool compound for exploring how triple agonists might reshape weight-loss curves, hunger signals, and long-term metabolic balance in advanced obesity models. PMC
2. GLP-3 and Type 2 Diabetes Markers
In people with type 2 diabetes, GLP-3 has been studied for its impact on blood sugar control and body weight within experimental clinical protocols. One phase 2 trial reported meaningful improvements in HbA1c (a long-term blood sugar marker) and robust reductions in body weight compared with placebo, with a safety profile similar to other incretin-based agents. PubMed
These findings suggest that GLP-3 peptide can be used as a research tool to examine how multi-receptor incretin agonists affect glucose handling, insulin sensitivity, and cardiometabolic risk markers. Even though these data come from human studies, they do not equal regulatory approval or established therapeutic use.
3. GLP-3 and Liver Fat / MASLD Models
Another important research focus for GLP-3 peptide is metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously known as NAFLD. In a phase 2 obesity study with a MASLD substudy, GLP-3 was associated with very large reductions in liver fat content (often over 80% relative reduction at higher doses) and a high rate of “resolution” of fatty liver by MRI criteria. PubMed
These data make GLP-3 attractive for labs exploring liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis pathways. Follow-up work is examining how triple agonists might influence long-term liver outcomes and whether they can shift biomarkers linked to steatosis, scarring, and metabolic syndrome risk. Nature Medicine
4. GLP-3 and Triple Agonist Innovation
GLP-3 is often discussed as a “next-generation” incretin-based research peptide. Review articles describe it as part of a broader move from single-receptor drugs to dual and triple agonists, seeking to combine appetite control, glucose regulation, and energy expenditure in one molecule. PMC
Because of this, GLP-3 peptide is frequently used in scientific discussions and models comparing GLP-1-only agents, GLP-2 dual agonists, and GIP/GLP-1/glucagon triple agonists. These comparisons help researchers understand which receptor combinations might deliver the strongest metabolic shifts with acceptable tolerability in controlled studies. ScienceDirect
GLP-3 Peptide Dosing Concepts for Lab Research
This section is educational, not prescriptive.
In research settings, dosing of GLP-3 peptide is usually based on the model being used (cell, animal, or clinical study) and the specific questions being asked. Investigators typically explore a range of doses to map out how metabolic, weight, or liver-fat markers change over time, rather than relying on a single fixed amount. Results from early phase trials often guide the choice of dose levels for later studies, but these remain experimental and not intended as medical guidance. PubMed
Focus: Standardizing how much peptide each model receives so results are easier to compare across time points and treatment groups.
Study design: Using time-course sampling (early vs later visits) and multiple arms (different doses or comparators) to understand dose-response relationships in metabolic and liver research.
Reconstitution: Use the peptide dosage calculator to plan vial reconstitution and aliquots.
GLP-3 Peptide Specifications Table
| Parameter | Details |
| Peptide name | GLP-3 |
| Vial content | 30 mg per vial (lyophilized powder) |
| Peptide type | Single peptide (triple hormone receptor agonist) |
| Typical use case | Metabolic, weight, and liver research models |
| Storage guidance | Cool, dry, dark; follow lab SOPs |
| Intended use | Laboratory research only, not for human use |
GLP-3 Peptide FAQs
What is GLP-3 peptide used for in research?
In research, GLP-3 peptide is mainly used to study advanced metabolic control. Scientists look at how it may influence body weight, appetite signals, blood sugar markers, and liver fat in various models, including animal studies and clinical trials. PubMed
How is GLP-3 peptide 30 mg per vial typically stored in a lab?
Labs usually store GLP-3 peptide 30 mg per vial as a lyophilized powder in a cool, dry, and dark environment. After reconstitution with a suitable sterile solvent, it is often kept refrigerated or frozen according to institutional SOPs and stability data, and labeled clearly as a research peptide only.
Is GLP-3 peptide similar to other incretin-based research peptides?
GLP-3 is related to GLP-1 and GLP-2 agonists but goes a step further by also activating the glucagon receptor. This “triple agonist” profile makes it distinct from single-receptor GLP-1 analogs and dual agonists, and it is being explored as part of a new class of multi-target metabolic agents. e-ENM
How does GLP-3 peptide differ from GLP-1 medications?
GLP-1 medications act mainly on the GLP-1 receptor. GLP-3, by contrast, targets GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors at the same time, which may lead to different patterns of weight change, blood sugar control, and liver fat outcomes in research models. PMC
Where to buy GLP-3 online?
You can buy GLP-3 online in the United States at Protide Health. Every compound is clearly labeled as a research peptide, backed by third-party testing, and intended only for controlled laboratory use—not for human consumption or medical treatment.
Conclusion: Summary of GLP-3 Peptide for Research
GLP-3 peptide is a next-generation, triple hormone receptor agonist supplied as a 30 mg per vial research peptide for advanced metabolic studies. By acting on GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors, it offers a unique way to explore appetite, blood sugar markers, energy expenditure, and liver fat in modern metabolic models. PubMed
Across obesity, type 2 diabetes, and fatty liver research, GLP-3 has generated strong interest as a tool for understanding how multi-target incretin-based approaches might shape future metabolic science. All work with GLP-3 peptide should remain within controlled laboratory and preclinical settings and is not intended for human use. PMC
Citations
Jastreboff AM et al., 2023. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist GLP-3 for Obesity – A Phase 2 Trial. New England Journal of Medicine.
Rosenstock J et al., 2023. GLP-3, a GIP, GLP-1 and glucagon receptor agonist, in people with type 2 diabetes. PubMed.
Sanyal AJ et al., 2024. Triple hormone receptor agonist GLP-3 for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease. Nature Medicine.
Abdul-Rahman T et al., 2024. GLP-3’s role in modern obesity and diabetes therapy. European Journal of Pharmacology.
Jakubowska A et al., 2024. GLP-1, GIP and glucagon receptor agonism in diabetes and obesity. Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Katsi V et al., 2025. GLP-3—A Game Changer in Obesity Pharmacotherapy. Frontiers in Endocrinology / PMC.
Legal Disclaimer
The information provided in this description is for research purposes only. The GLP-3 peptide is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or any regulatory authority for human consumption or therapeutic use. It is intended solely for investigational use in controlled laboratory settings by qualified researchers. Researchers must comply with all applicable local, state, and federal regulations, including obtaining necessary approvals for experimental use. Products sold by Protide Health are for laboratory research purposes only and are not intended for human consumption, medical use, or veterinary use.