MOTS-c 20mg
$100.00
In stock
Free shipping on orders over $149!
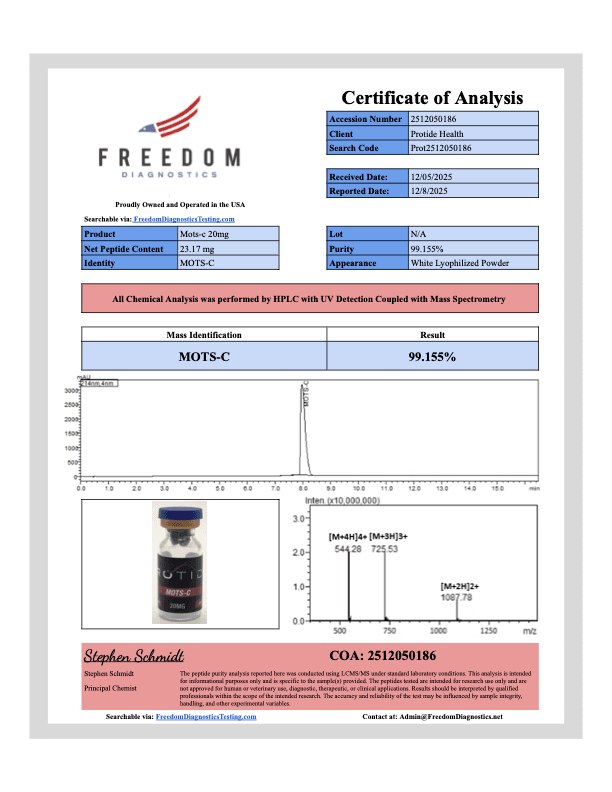
- 99% Purity
- Third-Party Tested
- Secure Payments
- Free BAC Water
- Satisfaction Guaranteed
What is MOTS-c?
MOTS-c peptide 20mg is a synthetic research peptide that matches a short sequence naturally made inside the mitochondria, the “power plants” of cells. In this listing, MOTS-c peptide is supplied as a 20mg lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder in a single research vial for reconstitution and use in controlled lab models only.
Researchers are studying MOTS-c peptide for its role in metabolism, insulin signaling, exercise capacity, and aging-related pathways in cell and animal systems, but it is not approved for human use or any medical purpose. Lee et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2019
- Peptide type: Single mitochondrial-derived research peptide studied in metabolic, exercise, and aging models.
- Vial content: 20mg MOTS-c peptide as a lyophilized powder in a sealed research vial.
- Primary research focus: Metabolism and insulin signaling, exercise performance, and aging-related stress responses in preclinical models.
MOTS-c Peptide Overview & Key Properties
MOTS-c is a 16-amino-acid mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP). In the body, it is encoded in the mitochondrial 12S rRNA region and acts like a small signaling hormone that helps cells respond to energy stress. Frontiers in Endocrinology review, 2023
The MOTS-c peptide 20mg offered here is a synthetic version designed for laboratory use. It arrives as a lyophilized powder that labs typically store cold and dry and reconstitute according to internal standard operating procedures (SOPs). In preclinical research, MOTS-c is often grouped with metabolism-focused research peptides that interact with energy and stress pathways such as AMPK. Lee et al., 2015
- Peptide class or family: Mitochondrial-derived peptide linked to cellular energy sensing and insulin sensitivity.
- Vial content and typical lab handling: Single 20mg vial of lyophilized powder, reconstituted and aliquoted under sterile lab conditions.
- Suggested storage concept in lab settings: Keep cool, dry, and protected from light; avoid unnecessary freeze–thaw cycles in line with lab SOPs.
- Common research models: Cell systems, rodent models of obesity and insulin resistance, exercise capacity models, and aging or cardiovascular models. Lee et al., 2015; Pham et al., 2025
Labs that need different quantities may also explore related vial sizes such as MOTS-c 10mg, depending on the design of their preclinical models.
MOTS-c Mechanism of Action
In simple terms, MOTS-c helps cells sense and adapt to energy stress in preclinical models. It appears to activate AMPK, a key energy-sensing enzyme that tells cells to use more glucose and fats for fuel and to improve metabolic balance. In animal studies, this AMPK-linked signaling has been associated with better insulin sensitivity and healthier glucose handling under high-fat diet stress. Lee et al., 2015; Pham et al., 2025
MOTS-c is unusual because it is encoded in mitochondrial DNA but can move to the nucleus when cells are under metabolic stress. Once in the nucleus, MOTS-c can bind chromatin and help regulate genes involved in antioxidant defenses and stress resistance, which may support cell survival in harsh conditions. Kim et al., 2018 This “mitonuclear” signaling is a major reason MOTS-c is of interest in aging and longevity research, although this work is still early and mainly preclinical. Frontiers in Endocrinology review, 2023
MOTS-c Peptide Research
Researchers look at MOTS-c peptide for several broad themes, all within controlled lab and preclinical settings. Results below come from animal, cell, or early human-related work and do not indicate approved medical uses.
1. MOTS-c and metabolic health models
In mouse models fed a high-fat diet, MOTS-c administration has been associated with better insulin sensitivity, improved glucose tolerance, and reduced fat gain compared with untreated animals. Lee et al., 2015 These studies suggest MOTS-c can act as an “exercise-mimetic” signal in skeletal muscle, helping glucose enter cells and supporting metabolic flexibility under stress.
Review articles describe MOTS-c as a “metabolic regulator” that influences whole-body energy use, insulin action, and body weight across multiple preclinical experiments. Frontiers in Endocrinology review, 2023; Kim & colleagues, 2019 Cohort studies have also reported links between circulating MOTS-c levels and markers such as fasting insulin and body mass index, though these are observational and do not prove cause and effect.
2. MOTS-c and exercise & muscle function
A high-impact study in Nature Communications found that exercise in humans increased MOTS-c levels in muscle and blood, and that MOTS-c treatment in mice improved treadmill running capacity and power output under both normal and high-fat diet conditions. Zhang et al., 2021 In these models, animals treated with MOTS-c ran longer and showed better performance than controls, especially under metabolic stress.
Other work suggests MOTS-c can directly modulate muscle metabolism, including glucose uptake and mitochondrial activity, sometimes through targets such as CK2 and AMPK in skeletal muscle. Pham et al., 2025; Kim et al., 2018 These findings make MOTS-c peptide a popular tool for labs interested in exercise-related and muscle-function research.
3. MOTS-c and aging & longevity research
Because MOTS-c levels appear to decline with age in both humans and mice, some studies frame it as a potential “aging-related” signal. Frontiers in Endocrinology review, 2023 In older mice, MOTS-c treatment has been associated with better physical performance, improved metabolic markers, and changes in body composition in treadmill and rotarod tests. Zhang et al., 2021
Additional preclinical work points to roles in stress resistance, antioxidant defense, and mitochondrial protection in aging tissues, including the heart. Pham et al., 2025 However, these are experimental findings under controlled conditions and do not show that MOTS-c slows aging in humans.
4. MOTS-c and emerging human data
Direct human intervention data on native MOTS-c are still very limited. Most of what is known comes from:
- Observational studies linking natural MOTS-c levels with insulin sensitivity or cardiovascular markers. Kim & colleagues, 2019
- A Phase 1a/1b clinical trial of CB4211, a MOTS-c analog, in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which reported that four weeks of treatment improved some liver and metabolic biomarkers and was generally well tolerated. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03998514; Loomba et al., AASLD abstract
These studies support the idea that the MOTS-c pathway is interesting for human metabolism, but they do not justify self-use or any medical claims. MOTS-c peptide 20mg remains a research-use-only compound.
MOTS-c Peptide Dosing Concepts for Lab Research
This section is educational, not prescriptive.
In published animal and cell studies, researchers typically select a range of MOTS-c doses, apply them over defined time periods, and then track changes in metabolic markers, exercise capacity, or tissue function. Study teams focus on consistent dosing across groups, clear control arms, and careful timing of sample collection, rather than on a single “perfect” amount. Lee et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2021
- Focus: Standardizing how much peptide each experimental model receives so results are easier to compare within and between studies.
- Study design: Using time-course sampling (early vs later time points), or comparing MOTS-c peptide versus vehicle or related analogs, to understand dose–response patterns and durability of effects.
- Use the peptide dosage calculator to plan vial reconstitution and aliquots.
No part of this section is intended as advice for human dosing or self-administration.
MOTS-c Peptide Specifications Table
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Peptide name | MOTS-c peptide |
| Vial content | 20mg (lyophilized powder) |
| Peptide type | Single peptide |
| Typical use case | Metabolic, exercise, and aging-related preclinical / in vitro models |
| Storage guidance | Cool, dry, dark; follow internal laboratory SOPs |
| Intended use | Laboratory research only, not for human use |
MOTS-c Peptide FAQs
What are the benefits of MOTS-c peptide?
In research settings, MOTS-c peptide has been associated with improved insulin sensitivity, better glucose handling, and reduced fat gain in high-fat diet mouse models. Lee et al., 2015 It has also been linked to better exercise performance and stress resistance in skeletal muscle in animal and cell studies. Zhang et al., 2021; Pham et al., 2025 These observations apply only to controlled research models and do not prove benefits for humans.
What are the side effects of MOTS-c peptide?
Most side-effect information comes from animal studies and from a small early-phase trial of CB4211, a MOTS-c analog, where safety and tolerability were the main endpoints. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03998514 In those settings, treatment was generally described as well tolerated, but detailed long-term safety data are still lacking. Because MOTS-c peptide 20mg is not approved for human use, there is no established human safety profile, and any non-research use would be experimental and risky.
Does MOTS-c increase testosterone?
Current MOTS-c research focuses on metabolism, insulin sensitivity, cardiovascular function, and exercise capacity. Frontiers in Endocrinology review, 2023 There is no strong evidence that MOTS-c directly increases testosterone in humans, and it is not studied or approved as a hormone or testosterone therapy. Any claims about testosterone effects should be viewed as speculative until robust clinical data exist.
Does MOTS-c build muscle?
In mouse studies, MOTS-c treatment has been linked to improved physical performance and, in some cases, changes in lean mass under high-fat diet stress. Zhang et al., 2021 Lab studies also suggest it can support muscle metabolism and stress resistance. Pham et al., 2025 However, these results do not mean MOTS-c peptide “builds muscle” in humans, and it is not an approved muscle-building or bodybuilding drug.
Can MOTS-c slow aging?
Preclinical work suggests that MOTS-c levels decline with age and that boosting the pathway in older animals may improve physical performance and some metabolic markers. Zhang et al., 2021; Frontiers in Endocrinology review, 2023 Some authors describe this as potential “healthspan” support in aging models. However, aging is complex, and there is no proof that MOTS-c slows or reverses aging in humans. It remains a research topic, not an anti-aging therapy.
Is MOTS-c worth taking?
From a research point of view, the MOTS-c pathway is very interesting and continues to attract new studies in metabolism and aging. But for individual use, MOTS-c peptide 20mg is not approved, has limited human data, and comes with unknown long-term risks. Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation summary, 2020 It should not be viewed as a supplement or therapy to “take”; it should only be handled in qualified labs under proper oversight.
How fast does MOTS-c work?
In mouse studies, some exercise and metabolic changes were seen over days to a few weeks of MOTS-c treatment under controlled dosing schedules. Zhang et al., 2021; Pham et al., 2025 In cell experiments, stress-resistance effects can appear within hours to days of exposure. Kim et al., 2018 These timelines are specific to lab models and do not translate into guidance for human use.
Where to buy MOTS-c online?
You can buy MOTS-c peptide for research use in the United States at Protide Health. Protide provides clearly labeled, third-party-tested research peptides, including MOTS-c peptide 20mg, for qualified labs. All products are sold strictly for laboratory and in vitro research, not for human consumption.
Is MOTS-c peptide legal to buy for research in the US?
In the United States, MOTS-c peptide is typically sold as a research-use-only chemical, not as a drug or supplement. Labs should confirm that their purchase and use comply with federal, state, and institutional rules, including any IRB or animal-care requirements. This product is not approved by the FDA for treating any condition.
How is MOTS-c peptide typically stored in a lab?
Vials of MOTS-c peptide 20mg usually ship as lyophilized powder and are stored in a cool, dry, and dark environment, such as a refrigerator or freezer, in line with lab SOPs. After reconstitution, many labs aliquot solutions and minimize freeze–thaw cycles to maintain peptide integrity. Exact storage and handling procedures should follow the institution’s internal quality and safety standards.
Conclusion: Summary of MOTS-c Peptide for Research
MOTS-c peptide 20mg is a single mitochondrial-derived research peptide supplied as a lyophilized powder for controlled laboratory use. It is studied for how it links mitochondrial signaling to energy balance, insulin sensitivity, exercise capacity, and cellular stress responses in preclinical models.
Across animal and cell studies, MOTS-c has emerged as a versatile tool for exploring metabolic disease, exercise performance, cardiovascular stress, and aging biology. Lee et al., 2015; Pham et al., 2025 At the same time, human evidence is still early, and MOTS-c peptide remains strictly a research-only compound, not for human use or any therapeutic application.
Citations
- Lee C. et al., 2015. The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c promotes metabolic homeostasis and reduces obesity and insulin resistance. Cell Metabolism. Europe PMC
- Kim S.J. & colleagues, 2019. MOTS-c: an equal opportunity insulin sensitizer. Journal of Molecular Medicine. Springer
- Kim K.H. et al., 2018. The mitochondrial-encoded peptide MOTS-c translocates to the nucleus to regulate gene expression in response to metabolic stress. Cell Metabolism. ScienceDirect
- Zhang et al., 2021. MOTS-c is an exercise-induced mitochondrial-encoded regulator of age-dependent physical decline and muscle homeostasis. Nature Communications. Nature
- Zheng Y. et al., 2023. MOTS-c: A promising mitochondrial-derived peptide for therapeutic exploitation. Frontiers in Endocrinology. Frontiers
- Pham T. et al., 2025. Mitochondria-derived peptide MOTS-c restores mitochondrial respiration in type 2 diabetic heart. Frontiers in Physiology. Frontiers
- Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, 2020. MOTS-c scientific evidence summary. AlzDiscovery
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A Phase 1a/1b Study of CB4211 in Healthy Non-obese Subjects and Subjects With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (MOTS-c analog). NCT03998514
Legal Disclaimer for MOTS-c Peptide
The information provided in this description is for research purposes only. The MOTS-c peptide is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or any regulatory authority for human consumption or therapeutic use. It is intended solely for investigational use in controlled laboratory settings by qualified researchers. Protide Health does not endorse or promote the use of MOTS-c peptide in humans or animals outside of approved research protocols. Researchers must comply with all applicable local, state, and federal regulations, including obtaining necessary approvals for experimental use. Consult with regulatory authorities before initiating any research involving MOTS-c peptide.
Products sold by Protide Health are for laboratory research purposes only and are not intended for human consumption, medical use, or veterinary use.
| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 1 × 1 × 1 in |