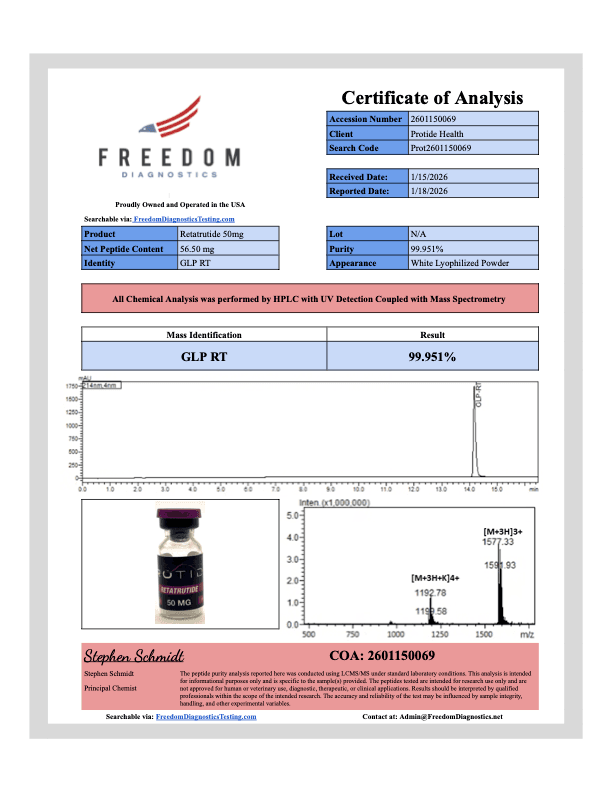
GLP-3 50mg
$330.00
In stock
Free shipping on orders over $149!
- 99% Purity
- Third-Party Tested
- Secure Payments
- Free BAC Water
- Satisfaction Guaranteed
What is GLP-3?
GLP-3 is a synthetic research peptide designed to help labs study how multiple gut-hormone signals can work together in metabolic models. This GLP-3 peptide is supplied as a vial for controlled laboratory and preclinical research use.
Because GLP-3 is studied in the same “multi-receptor” category as next-generation incretin agonists, it often appears in research peptides work focused on appetite signaling, energy balance, and biomarker shifts in controlled study designs.
Peptide type: single peptide, engineered “multi-receptor” incretin-style research tool.
Vial content: 50mg (lyophilized powder).
Primary research focus: energy balance and metabolism models, appetite and intake signaling models.
GLP-3 Peptide Overview & Key Properties
GLP-3 is a lab-designed (synthetic) peptide created to mimic and combine signals that are normally triggered by gut hormones after eating. In simple terms, researchers use this class of peptides to study how the body regulates hunger cues, glucose handling, and energy use in preclinical settings. Published research describes this type of triple-receptor agonism as involving GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptor activity. For example, a phase 2 clinical study evaluated a triple–hormone-receptor agonist in adults with obesity; this is human research data but it does not mean the compound is approved for medical use. Jastreboff et al., 2023
GLP-3 is typically provided as a lyophilized powder (freeze-dried) and is commonly kept cold, dry, and protected from light in lab settings to support stability and consistent handling.
Peptide class or family: incretin-style, multi-receptor agonist research peptide (studied for combined satiety + energy signaling).
Vial content and typical lab handling: 50mg lyophilized powder, handled using sterile technique and lab SOPs.
Suggested storage concept in lab settings: cool, dry, dark; minimize temperature swings and moisture per SOPs.
Common research models: cell studies, animal models, and controlled human research settings (human data does not equal approved use).
GLP-3 Mechanism of Action
GLP-3 is studied as a “triple-agonist style” signal in research, meaning it is designed to activate more than one hormone receptor pathway that influences energy balance. In plain language, these pathways can tell the brain and body, “food is coming in,” which may shift appetite signals, slow stomach emptying, and change how nutrients are processed in models. Reviews on GLP-1 biology and satiety describe how GLP-1 signaling can shape appetite and stomach emptying in research settings. Holst, 2024
The “third signal” often discussed in this research category is glucagon receptor activity, which is associated with energy use (how much fuel the body burns) in preclinical models. A mechanistic paper describing a triple agonist (GLP-1/GIP/glucagon) reports that adding glucagon receptor activity may increase energy expenditure alongside reduced intake signals. Coskun et al., 2022
GLP-3 Peptide Research
1. GLP-3 and Body Weight Models
In controlled research, triple-receptor agonist designs have been evaluated in adults with obesity as well as in preclinical work. A published phase 2 trial reported substantial body-weight reductions over time in adults with obesity for a triple–hormone-receptor agonist, with outcomes measured across multiple dose groups. This is human clinical research and does not indicate FDA approval or permission for non-research use. Jastreboff et al., 2023
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses have also summarized trial outcomes for this compound class and reported meaningful shifts in weight and metabolic markers across included studies, while noting the need for larger and longer trials. Systematic review, 2025
2. GLP-3 and Energy Expenditure Models
One reason researchers are interested in triple-receptor designs is the hypothesis that combining satiety signaling (feeling full) with energy-use signaling may produce different outcomes than single-pathway incretin approaches in animal models. In obese mice, a triple agonist reported improved weight outcomes, with the work describing a role for glucagon receptor activity in supporting higher energy expenditure (how much energy the body burns). Coskun et al., 2022
Related preclinical research on GLP-1/GIP/glucagon triagonists also reports improvements in weight and energy expenditure in diet-induced obesity mouse models, compared with simpler agonist designs. Tschöp et al., 2022
3. GLP-3 and Appetite Signaling Models
GLP-1 signaling is widely studied for its role in appetite regulation and satiation (the “I’m full” signal). Research reviews describe how incretin hormones and GLP-1 pathways influence food intake and meal-size behavior in lab and translational models. Gribble & Reimann, 2013
Researchers often frame triple-agonist designs as a way to explore how multiple appetite-related pathways may interact, including how signals relate to nausea, satiety, and downstream intake behavior. GIP and satiety review
GLP-3 Peptide Dosing Concepts for Lab Research
This section is educational, not prescriptive.
In research settings, dosing is typically planned around the study goal (what outcome is being measured), the model used (cell, animal, or controlled clinical research), and the time course (how long observations run). Researchers commonly test more than one dose level to compare response patterns over time and to understand tolerability signals inside the model being used.
Focus: standardizing how much peptide each model receives so results are easier to compare.
Study design: using time-course sampling (early vs later time points) and comparing outcomes across dose groups.
GLP-3 Peptide Specifications Table
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Peptide name | GLP-3 peptide |
| Vial content | 50mg (lyophilized powder) |
| Peptide type | Single peptide |
| Typical use case | Metabolic and energy-balance preclinical models |
| Storage guidance | Cool, dry, dark; follow lab SOPs |
| Intended use | Laboratory research only, not for human use |
GLP-3 Peptide FAQs
What is GLP-3 peptide used for in research?
GLP-3 peptide is commonly studied in metabolic research models focused on appetite signaling, energy balance, and related biomarkers. Labs may use it to explore how combined incretin-style pathways behave compared to simpler single-pathway designs. Results depend heavily on the model, dosing plan, and study length.
Is GLP-3 peptide the same as GLP-1 peptides?
Not exactly. GLP-1 refers to one specific hormone pathway that is widely studied for appetite and glucose signaling. GLP-3 is used here as a label for a multi-receptor, incretin-style research peptide design that is discussed in the scientific literature as engaging more than one pathway.
How is GLP-3 peptide typically stored in a lab?
Most labs store lyophilized peptides cold, dry, and protected from light to help maintain stability. After reconstitution, storage and handling should follow your lab’s SOPs for sterility, temperature control, and documentation.
What kinds of studies exist on triple-receptor incretin agonists?
There are published preclinical studies in animal models and published human clinical research for a triple–hormone-receptor agonist design, including a phase 2 trial in adults with obesity. Human research findings do not mean the compound is approved for medical use or appropriate outside controlled research settings.
Can GLP-3 be used in cell studies?
Many labs use incretin-style peptides in cell-based assays when exploring receptor signaling, downstream pathways, and biomarker shifts. Whether a specific cell model is appropriate depends on receptor expression and the assay design.
Where to buy GLP-3 online?
You can buy GLP-3 online in the United States at Protide Health. Every compound is backed by science, clearly labeled, and third-party tested.
Conclusion: Summary of GLP-3 Peptide for Research
GLP-3 peptide is a 50mg research peptide used in studies exploring combined incretin-style signaling in metabolic and energy-balance models. Researchers typically focus on appetite signaling, intake behavior, and energy expenditure concepts in preclinical designs.
GLP-3 is intended only for controlled laboratory and preclinical research use by qualified professionals, and it is not approved for human use.
Citations
Jastreboff AM et al., 2023. Triple–hormone-receptor agonist in adults with obesity (phase 2). PubMed
Jastreboff AM et al., 2023. Phase 2 trial full text (peer-reviewed journal). New England Journal of Medicine
Coskun T et al., 2022. Triple GLP-1/GIP/glucagon receptor agonist preclinical + phase 1 findings. PubMed
Systematic review & meta-analysis, 2025. Safety/efficacy summary across randomized trials. PubMed
Tschöp MH et al., 2022. GLP-1/GIP/glucagon triple agonists in diet-induced obesity mouse models. PMC (NIH)
Gribble FM, Reimann F, 2013. Incretin hormones and satiation signaling (review). PMC (NIH)
Holst JJ, 2024. Reflections on GLP-1 as a satiety hormone (review). PubMed
GIP/GLP-1 satiety & nausea pathways (review). PMC (NIH)
Legal Disclaimer for GLP-3 Peptide
The information provided in this description is for research purposes only. The GLP-3 peptide is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or any regulatory authority for human consumption or therapeutic use. It is intended solely for investigational use in controlled laboratory settings by qualified researchers. Protide Health does not endorse or promote the use of GLP-3 peptide in humans or animals outside of approved research protocols. Researchers must comply with all applicable local, state, and federal regulations, including obtaining necessary approvals for experimental use. Consult with regulatory authorities before initiating any research involving GLP-3 peptide.
Products sold by Protide Health are for laboratory research purposes only and are not intended for human consumption, medical use, or veterinary use.
| Weight | 1 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 1 × 1 × 1 in |