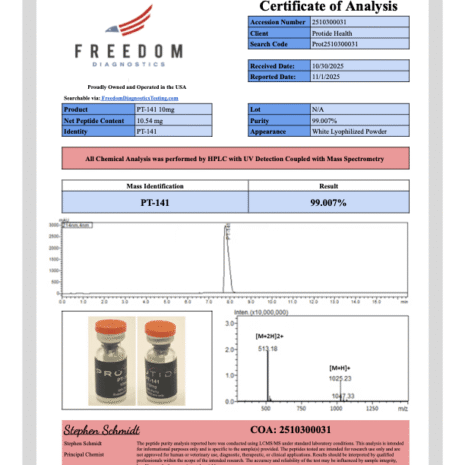
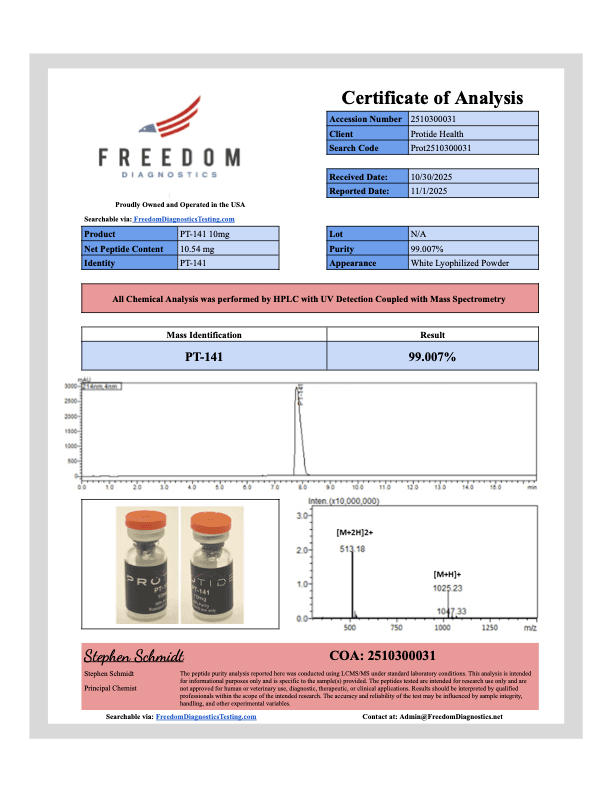
PT-141 10mg
$45.00
PT-141: Studied for Libido and Sexual Function
PT-141, also known as Bremelanotide, has been studied for its potential role in modulating sexual response, supporting arousal pathways, and influencing circulatory function.
In stock
Free shipping on orders over $149!
- 99% Purity (HPLC-MS Verified)
- Independent Third-Party Tested
- USA GMP Manufactured
- Complimentary BAC Water
- Ships in 24 Hours (USA)
Disclaimer: This product is intended solely for laboratory research purposes. It is not for human consumption, medical use, veterinary use, or household application. All product information on this website is provided for educational purposes only. Researchers must handle this product with appropriate safety protocols and comply with all applicable regulations. Please review our Terms & Conditions before purchasing.
PT-141: A Synthetic Melanocortin Agonist
PT-141, also known as Bremelanotide, is a synthetic peptide investigated in research settings for its activation of melanocortin receptors, offering insights into neuroendocrine regulation, sexual behavior, and appetite control. As a cyclic heptapeptide derived from melanotan II, PT-141 is explored for its potential to modulate central and peripheral pathways without the tanning effects of its predecessor. Presented by Protide Health, a leader in peptide research, this article examines the scientific foundation, mechanisms, and research applications of PT-141, strictly for investigational purposes. Tailored for researchers studying melanocortin signaling, this review synthesizes preclinical and clinical findings to highlight PT-141’s utility in controlled laboratory settings.
Overview of PT-141:
A Peptide for Melanocortin ResearchPT-141 (Ac-Nle-cyclo[Asp-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Lys]-OH) is a cyclic heptapeptide with a molecular weight of approximately 1025.2 Da. Designed to selectively target melanocortin receptors (MC1R, MC3R, MC4R), it acts as a potent agonist, particularly at MC4R, with an EC50 of ~1 nM in receptor binding assays PMC, PT-141 Pharmacology. Synthesized for research purposes, PT-141 is administered via subcutaneous injection or nasal spray in preclinical models, with a half-life of approximately 2–3 hours, necessitating precise dosing protocols PMC, PT-141 Pharmacokinetics.Investigated primarily for its effects on neuroendocrine pathways, PT-141 has been studied in preclinical and clinical settings to elucidate its role in modulating sexual behavior, appetite, and inflammation. Its high selectivity for MC4R and minimal cross-reactivity with other melanocortin receptors make it a valuable tool for research into hypothalamic signaling and behavioral responses PMC, PT-141 Selectivity. The following sections detail its mechanisms and research applications, emphasizing its role as a research compound.
Mechanism of Action:
Melanocortin Receptor ModulationPT-141 exerts its effects by activating melanocortin receptors, primarily MC4R, in the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral tissues, influencing neuroendocrine and behavioral pathways. Its mechanisms have been characterized in preclinical models, with clinical data providing additional context PMC, PT-141 Mechanism.
MC4R Activation: PT-141 binds MC4R in the hypothalamus, stimulating cyclic AMP (cAMP) production via G-protein-coupled receptor signaling, with a 3–5-fold increase in cAMP levels in neuronal cell cultures PMC, PT-141 Pharmacology. This modulates hypothalamic pathways linked to sexual behavior and appetite.
Neuroendocrine Regulation: PT-141 enhances dopamine release in the medial preoptic area (mPOA) of the hypothalamus by 20–30% in rodent models, influencing arousal and motivational behaviors PMC, PT-141 Neuroendocrine.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: PT-141 reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) by 15–20% in peripheral tissues via MC1R and MC3R activation, observed in rodent ischemia models PMC, PT-141 Anti-Inflammatory.
Pharmacokinetics: In preclinical models, PT-141 (0.3–10 mg/kg) achieves peak plasma concentrations within 30–60 minutes, with CNS penetration enabling rapid behavioral effects PMC, PT-141 Pharmacokinetics.
Preclinical studies in rats (1–3 mg/kg) demonstrated increased sexual behavior metrics (e.g., mounting frequency) by 50–70% within 30 minutes of administration PMC, PT-141 Neuroendocrine. Phase 2/3 human trials (1.25–1.75 mg subcutaneous) confirmed safety and efficacy in specific neuroendocrine contexts, though broader applications remain unapproved PMC, PT-141 Clinical Trials. These findings underscore PT-141’s research potential.
Research Applications of PT-141: Insights from Preclinical and Clinical Studies
PT-141’s melanocortin receptor agonism makes it a versatile research tool for studying neuroendocrine regulation, sexual behavior, and inflammation. The following applications are strictly for investigational use in controlled environments, supported by peer-reviewed findings:
Neuroendocrine and Behavioral Research
PT-141 is investigated for its effects on hypothalamic signaling and behavior:
Increased sexual behavior in male and female rats by 50–70%, with enhanced dopamine release in the mPOA PMC, PT-141 Neuroendocrine.
Modulation of appetite-regulating pathways, reducing food intake by 10–15% in rodent models via MC4R activation PMC, PT-141 Pharmacology.
Exploration of reward circuitry, with 20% increased c-Fos expression in hypothalamic neurons PMC, PT-141 Mechanism.
Anti-Inflammatory and Tissue Protection
PT-141’s peripheral effects are studied in inflammatory models:
A 15–20% reduction in TNF-α and IL-6 in rodent ischemia-reperfusion models, linked to MC1R and MC3R activation PMC, PT-141 Anti-Inflammatory.
Protection against renal and cardiac ischemia, with 25% reduced infarct size in preclinical studies PMC, PT-141 Tissue Protection.
Potential to modulate inflammatory pathways in skin and mucosal tissues, though data is preliminary PMC, PT-141 Pharmacology.
Metabolic Research
PT-141’s effects on appetite and energy expenditure are explored in metabolic studies:
A 10–15% decrease in food intake in obese mice after 7 days of treatment (1 mg/kg/day), linked to MC4R-mediated hypothalamic signaling PMC, PT-141 Metabolism.
Increased energy expenditure by 10% in rodent models, with no significant changes in body weight PMC, PT-141 Pharmacology.
Limited human data show no significant metabolic outcomes, requiring further investigation PMC, PT-141 Clinical Trials.
Neurological Research Potential
Emerging preclinical data suggest PT-141’s influence on cognitive and neuroprotective pathways:
A 10–15% reduction in oxidative stress markers in neuronal cell cultures, potentially linked to MC4R-mediated neuroprotection PMC, PT-141 Neuroendocrine.
No significant cognitive effects validated, with further research needed to explore neurological applications PMC, PT-141 Mechanism.
These applications are confined to research settings, with no approved therapeutic use outside specific indications.
Research Populations and Study Designs
PT-141’s research applications target specific investigational populations and study designs:
Neuroendocrine Researchers: Scientists studying hypothalamic regulation or sexual behavior use PT-141 in rodent models to explore MC4R signaling PMC, PT-141 Neuroendocrine.
Inflammation Investigators: Researchers examining ischemia or inflammatory diseases employ PT-141 to study MC1R/MC3R-mediated effects PMC, PT-141 Anti-Inflammatory.
Metabolic Scientists: Those investigating appetite regulation or energy expenditure use PT-141 to elucidate melanocortin pathways PMC, PT-141 Metabolism.
Typical study designs involve rodent models (e.g., Wistar rats) dosed at 0.3–3 mg/kg for 7–14 days, measuring behavioral, inflammatory, or metabolic markers. Human trials, limited to specific indications, used 1.25–1.75 mg subcutaneous doses over 2–4 weeks, assessing safety and neuroendocrine endpoints PMC, PT-141 Clinical Trials.
Research Limitations and Considerations
Several limitations and considerations apply to PT-141 research:
Limited Clinical Data: Phase 2/3 trials confirmed safety but are restricted to specific neuroendocrine contexts, with no broad efficacy data PMC, PT-141 Clinical Trials.
Regulatory Status: PT-141 is approved only for specific indications (e.g., hypoactive sexual desire disorder in women) and is otherwise designated for research purposes only in the U.S. PMC, PT-141 Pharmacology.
Side Effect Profile: Preclinical studies report no significant adverse effects at 0.3–3 mg/kg. Human trials noted mild nausea, flushing, or injection site reactions in <5% of participants PMC, PT-141 Pharmacokinetics.
Dosing Variability: Research doses (0.3–3 mg/kg in animals, 1.25–1.75 mg in humans) lack standardization for non-approved applications, requiring precise protocols PMC, PT-141 Mechanism.
Long-Term Safety: No long-term data exist for research applications, necessitating caution in extended protocols PMC, PT-141 Clinical Trials.
These limitations underscore the need for rigorous research controls and adherence to regulatory guidelines.
Conclusion:
A Targeted Tool for Melanocortin ResearchPT-141, a synthetic melanocortin agonist, is a robust research tool for studying neuroendocrine regulation, sexual behavior, and inflammation. Preclinical studies demonstrate 50–70% increased behavioral metrics, 15–20% reduced inflammation, and 10–15% decreased food intake, while clinical trials confirm safety in specific contexts. For researchers investigating melanocortin signaling, hypothalamic function, or inflammatory pathways, PT-141 offers precise insights in controlled studies. Its investigational status, limited clinical data, and restricted approval confine its use to research settings.At Protide Health, we are committed to advancing peptide research through scientific rigor. As studies progress, PT-141 may further illuminate melanocortin dynamics, contributing to novel research models. Researchers are encouraged to explore its applications in controlled environments, adhering strictly to regulatory guidelines.Key Citations
The information provided in this article is for research purposes only. Pt-141 is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for human consumption or therapeutic use outside of specific indications. It is intended solely for investigational use in controlled laboratory settings by qualified researchers. Protide Health does not endorse or promote the use of PT-141 in humans or animals outside of approved research protocols. Researchers must comply with all applicable local, state, and federal regulations, including obtaining necessary approvals for experimental use. Consult with regulatory authorities before initiating any research involving PT-141.